Ultimate Guide to Rainwater Filtration for Gardens
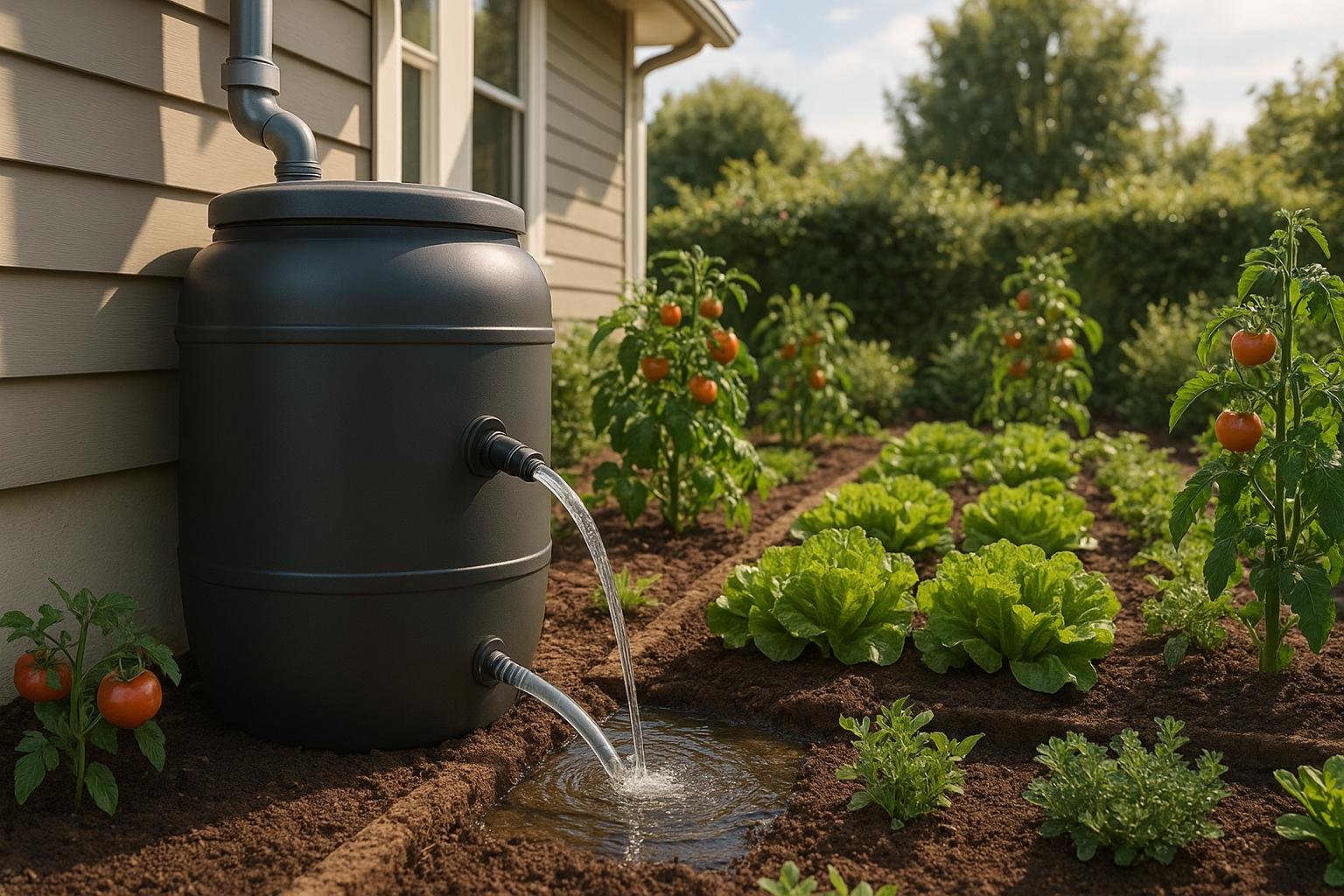

Rainwater filtration is a game-changer for gardeners, offering a natural, cost-effective way to water plants while reducing environmental impact. Here’s what you need to know:
-
Why Use Filtered Rainwater?
- It’s free of chemicals like chlorine and fluoride, promoting healthier plant growth.
- A 1,000 sq. ft. roof can collect over 620 gallons of water from just 1 inch of rain.
-
Key Benefits:
- Reduces stormwater runoff and urban flooding.
- Saves money by cutting reliance on municipal water.
- Slightly acidic pH improves nutrient absorption for plants.
-
How It Works:
- Collection: Roofs (preferably metal or clay tiles) and gutters gather rainwater.
- Pre-Filtration: Gutter screens, downspout filters, and first flush diverters remove debris.
- Storage & Filtration: Water is stored in tanks and passed through filters like UV disinfection or carbon filters.
-
Costs:
- Basic systems start at $75, while advanced setups can cost $8,000–$15,000.
- Maintenance includes cleaning filters, tanks, and checking for damage.
-
Irrigation Compatibility:
- Match filtration to your irrigation system (e.g., 120 mesh for drip emitters).
- Gravity-fed systems work for drip irrigation; pumps are needed for sprinklers.
Regular maintenance ensures clean water and smooth operation. Start simple, expand as needed, and enjoy the benefits of sustainable gardening.
Whole House Water Filter Install for my Rainwater Harvesting System

Rainwater Filtration System Basics
A properly designed rainwater filtration system includes several essential components that work together to provide clean water for your garden. Understanding the basics of how these systems function can help you make smarter choices about setup and upkeep.
Basic Filtration Process
Rainwater passes through a series of filtration steps, starting at the catchment area - usually your roof - and progressing through the following stages:
- Collection Phase Your roof and gutters serve as the first collection point. Surfaces like metal or clay tile roofs are preferred because, unlike asphalt shingles, they don’t release harmful chemicals into the water.
-
Pre-Filtration Stage
This step removes larger debris before the water enters the storage system. Common pre-filtration tools include:
- Gutter screens to block leaves and large debris.
- Downspout filters equipped with 500-micron screens to capture smaller particles.
- First flush diverters to redirect the initial runoff, which tends to carry more contaminants.
- Storage and Secondary Filtration After pre-filtration, water flows into storage tanks, where additional filters help maintain its quality.
Now, let’s explore the types of filters used in these systems.
Common Filter Types
Modern rainwater filtration systems combine various filters to ensure the water remains clean and safe. Below is a breakdown of commonly used filters and their roles:
| Filter Type | Primary Function |
|---|---|
| Mechanical Pre-tank | Captures debris before water enters storage. |
| Microscopic/Particulate | Filters out fine particles. |
| UV Disinfection | Kills bacteria and other microorganisms. |
| Carbon | Enhances clarity and removes odors. |
Must-Have System Features
For an effective garden filtration setup, certain components and monitoring tools are essential:
Primary Features:
- Mesh gutter guards to block large debris.
- Downspout filters with at least a 500-micron rating.
- A vertically mounted first flush diverter to handle contaminated initial runoff.
- Opaque storage tanks to minimize algae growth.
Monitoring Elements:
- Water level indicators for tracking storage capacity.
- Pressure gauges for systems using pumps.
- Filter status indicators to alert you when cleaning or replacement is needed.
Maintenance Matters
Regular maintenance is key to keeping your filtration system running smoothly. Here’s a quick guide to essential tasks:
| Component | Maintenance Task | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Collection System & Inlet Filter | Remove debris and inspect for damage. | Weekly |
| Storage Tank | Check for damage and clean out sediment. | Annually |
| Overflow System | Clear blockages and ensure proper function. | Monthly |
| Pump (if installed) | Test operation and lubricate parts. | Monthly |
Adding overflow protection and ensuring easy access for maintenance will boost the system’s efficiency. A consistent maintenance routine keeps everything in top shape and ensures reliable performance.
How to Choose Your Filtration System
Selecting the right filtration system involves evaluating your water needs, budget, and local weather conditions. Here’s how to approach it step by step.
Calculate Water Requirements
Start by determining how much water your garden requires. On average, a 100 ft² garden needs about 62 gallons of water per inch of rain. Keep in mind that plant water needs can change depending on factors like their growth stage, soil type, and whether you’re using mulch to retain moisture.
For precise tracking, consider installing a water meter. This will give you accurate data on your water usage and help you plan your system more effectively.
Price and Cost Analysis
The cost of a filtration system can vary widely depending on the components and complexity. Here's a breakdown of typical expenses:
| Component | Cost Range | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Filtration System | $75 - $200 | Covers only essential parts |
| Rain Barrels | $120 - $160 | A simple, entry-level solution |
| Complete Dry System | $1,000 - $5,000 | Includes a basic setup |
| Complete Wet System | $8,000 - $15,000 | Comes with advanced features |
| Storage Tank (5,000 gal) | $2,000 - $4,000 | Made from polyethylene material |
Installation Costs:
- Professional plumber: $75 - $130 per hour
- Landscaper installation: $50 - $100 per hour
- Excavation (if needed): $440 - $760 for three hours
While cost is a major factor, you’ll also need to consider your local rainfall patterns, as they directly influence the system’s required capacity.
Local Weather Impact
Your region's climate plays a big role in designing an efficient filtration system. To account for local weather, you should:
- Track annual rainfall levels.
- Observe how rainfall is distributed throughout the year.
- Plan to store enough water for dry periods.
For instance, rainfall in northern areas has increased by 10–40%, while southern regions are experiencing up to 20% drier conditions. This means you may need larger storage tanks in drier climates to ensure an adequate water supply during periods of low rainfall.
🚀 Ready to Reinvent Your Garden?
Join thousands of homeowners who have transformed their gardens using our AI design tool. Upload one photo to explore endless possibilities.
Get your AI garden designs →System Maintenance Guide
Once your system is installed and running, keeping it in top shape requires consistent maintenance. Regular upkeep not only ensures smooth operation but also helps you avoid expensive repairs down the road. Plus, it guarantees a steady supply of clean water for your needs.
"Regular inspection of your system is the most important aspect of maintenance. Frequent and thorough inspections are crucial to identifying potential issues early."
– Chris Maxwell-Gaines, Civil Engineer, Innovative Water Solutions LLC
Cleaning Schedule
Cleaning your system on a routine basis is essential, and the timing often depends on seasonal patterns and local conditions. Here’s a general guideline:
- Gutters: Clean them at least every six months. If you have overhanging trees, you might need to do it more often.
- First Flush Diverters: Rinse their screens 2–4 times a year, especially after heavy rains. This helps maintain proper water flow and prevents debris from clogging the system.
- Roofs and Gutters: Inspect and clean these areas 2–4 times annually, paying particular attention to spots like gutter-downspout junctions where debris tends to collect.
- Storage Tanks: Check for sediment buildup and algae growth 2–4 times a year. A deep clean during the off-season can help maintain water quality.
Parts Replacement Guide
Replacing components on time is just as important as cleaning. Overused or worn-out parts can compromise your system’s performance. Here’s what to keep in mind:
- Sediment Filters: Replace these monthly or quarterly, depending on your system's size and water usage.
- Carbon Filters: Change them 2–4 times a year to keep odors and chemical contaminants in check.
- Potable Water Systems: For drinking water, replace filters every six months and UV bulbs annually to ensure proper disinfection.
- Gutter Guards and Leaf Screens: Clean them regularly and check for any damage. For instance, Practical Preppers recommends maintaining Leaf Relief gutter guards in their filtration systems to prevent clogging and bacterial buildup.
Be alert to signs like odd odors, visible scale, debris, or strain on filters. These can indicate it’s time to replace certain parts.
"The best water filtration systems (such as the ones we provide) can last for years. However, it's important to know when to replace your system."
– Anglian Pumping Services
Water Testing Steps
After cleaning and replacing system components, testing the water is critical to ensure everything is working as it should. Regular testing helps you spot potential issues early and ensures the water meets safety standards for its intended use.
- E. coli Testing: This is especially important for gardens, schools, or community projects where regulations may apply. Always collect samples from the rain barrel’s faucet or hose connection for an accurate representation of the water being used.
- Sample Handling: If testing for pathogens, keep samples chilled in a cooler with ice and deliver them to the lab within six hours. Your local health department can guide you on E. coli testing services or certified labs.
- Safe Levels: For irrigation, E. coli levels should stay under 235 counts per 100 mL. In a New Jersey study, only 9% of rain barrel samples exceeded these federal standards.
Additional tests for pH, turbidity, and microbial presence can provide more insights into water quality. Rainwater’s natural softness and slight acidity can even benefit plant nutrient absorption. When arranging testing, specify that the water is for irrigation, not drinking.
sbb-itb-4d6a8dd
Connecting to Garden Irrigation
Link your filtration system to your garden's irrigation setup to use purified rainwater. This not only nourishes your plants but can also help lower your water bills.
Filter and Irrigation Compatibility
To ensure your filtration system works seamlessly with your irrigation method, it’s essential to match the filtration needs to the specific watering approach. Different irrigation products have unique requirements based on their orifice sizes and water pressure demands.
Pressure and Filtration Requirements
The type of irrigation you use dictates the filtration level needed to prevent clogs:
| Irrigation Product Type | Minimum Filtration Needed |
|---|---|
| Rotors, Sprinkler Spray Nozzles | 80 Mesh |
| Drip Emitters, Sprayers, Spray Jets | 120 Mesh |
| Drip Tape | 155 Mesh |
If your system combines multiple irrigation types, always filter to the smallest orifice size to ensure smooth operation across all components.
Selecting the Right Filter
The choice between disc and screen filters depends on the type of debris in your water. Screen filters are great for solid debris like leaves, sticks, and sediment. On the other hand, disc filters are better suited for organic contaminants such as algae or bacterial buildup. For typical rainwater systems, screen filters are often simpler to use and more cost-effective.
Pump vs. Gravity Systems
Sprinkler systems require a pump to achieve adequate pressure, while drip systems can function with gravity-fed setups using non-compensating drip lines. If you decide to use a pump, be sure to install a pressure regulator to avoid over-pressurizing and damaging your irrigation components.
Next, focus on designing an efficient water flow layout for your garden.
Water Flow Layout Tips
A well-planned water distribution layout ensures consistent and efficient irrigation.
Elevation and Pressure Optimization
Raising rain barrels above your irrigation area can improve water pressure - each foot of elevation adds approximately 0.43 PSI. Positioning barrels on an incline or uphill from garden beds can significantly enhance distribution. Gravity-fed systems have demonstrated success with these principles.
Distribution Patterns
To maintain even water flow in gravity-fed systems, use high-flow valves and fittings. Instead of relying on a single drip line, design a grid or forked pattern with multiple lines. This approach reduces pressure loss and ensures better coverage. Whenever possible, place main distribution lines to take advantage of natural downhill slopes, as even slight slopes can improve flow throughout the system.
Timing Adjustments
Gravity-fed systems typically operate at lower pressure (0–2 PSI) compared to pressurized systems (12–20 PSI). This means you might need to extend watering times to deliver the same amount of water. The slower flow rate, however, allows for better absorption by plants and helps reduce runoff.
Use these tips to design an effective system layout, and take advantage of the tools described below.
AIGardenPlanner Setup Tools
Once your irrigation layout is optimized, AIGardenPlanner can help you fine-tune your system’s design. Planning ahead can save money and ensure water is distributed efficiently across your garden.
Garden Layout Analysis
By uploading photos of your garden, AIGardenPlanner provides a complete overview of your irrigation needs. The AI Plant Advisor offers plant suggestions tailored to your local climate and rainfall, helping you identify areas that would benefit most from rainwater irrigation. With over 50 garden styles to choose from - including layouts that prioritize water conservation - the platform helps you maximize the use of filtered rainwater in your garden.
System Integration Planning
The platform also helps you strategically position rain barrels, filters, and distribution lines. Its tools allow you to visualize how elevated storage tanks can fit into your landscape while maintaining visual appeal. You can access detailed growing guides and maintenance schedules to align irrigation timing with your plants’ seasonal needs. For landscapers working on larger projects, AIGardenPlanner offers commercial licenses and high-resolution downloads to assist with client presentations and system installations.
Summary and Next Steps
Now that you've got the basics down, it's time to put your rainwater filtration system into action using the guidance from earlier sections.
Key Steps for Installation
Start by revisiting the setup instructions to ensure everything is installed correctly. If you're planning to use pressurized irrigation - like a drip system - you'll need a pump to maintain the right water flow. These steps align with your goals of efficient garden irrigation and long-term water conservation.
Keeping Your System in Top Shape
Regular maintenance is the key to keeping your system running smoothly. After heavy rains, inspect for blockages and clean any clogged components. Seasonal upkeep is also vital - unplug pumps and drain any trapped water before winter to prevent freeze damage.
If you'd prefer a structured approach, companies like Innovative Water Solutions LLC offer maintenance programs that include filter changes, UV lamp replacements, and system inspections. You can either use their professional services or follow their detailed documentation to handle it yourself.
Saving Money and Water
Once your system is up and running, you'll start seeing the benefits. Rainwater filtration can help lower your water bills, reduce reliance on municipal water, and improve the health of your plants. If you're using the water for edible plants, it’s a good idea to test its quality periodically to ensure it's safe.
Designing Your System Layout
To make the most of your setup, use rainwater harvesting calculators to estimate how much water you can collect based on your roof size and local rainfall. Storage capacity calculators can help you choose the right tank size by analyzing your catchment area and water usage patterns. For a more advanced approach, tools like AIGardenPlanner can help you map out barrel placement, distribution lines, and how the system fits into your landscape.
Start simple and expand as needed. Routine maintenance will protect your investment and ensure your system supports sustainable irrigation for years to come.
FAQs
How do I choose the right rainwater filtration system for my garden?
🎨 Visualize Your Dream Garden Today!
Transform any outdoor space into a professional landscape design in minutes. Just upload a photo, choose your style, and let our AI do the rest.
Start your garden transformation now →Choosing the Right Rainwater Filtration System for Your Garden
Start by figuring out how much water your garden needs. For instance, a vegetable garden typically requires about 1 inch of water per week. That’s approximately 0.62 gallons per square foot of garden space. Multiply this number by your garden's total square footage to get a clear picture of your weekly water demand.
Next, take a look at your roof. The size and material of your roof play a big role in how much rainwater you can collect. Metal roofs are the most efficient, capturing about 95% of rainfall, while shingles and tiles tend to collect slightly less. Combine this with your region’s average annual rainfall to estimate the total water you can harvest.
Lastly, choose a filtration system that aligns with your storage capacity and water quality requirements. The right system will deliver clean, safe water for your garden without unnecessary costs for extra capacity you won’t use.
What maintenance is required for a rainwater filtration system to keep it running efficiently over time?
How to Maintain Your Rainwater Filtration System
Keeping your rainwater filtration system in good shape requires consistent upkeep. Start by clearing out gutters and downspouts at least twice a year to avoid clogs and debris buildup. Filters need attention too - inspect and clean them monthly, or more frequently if necessary, and replace them as needed to ensure the water stays clean and safe.
Once a year, take time to examine your storage tank. Look for leaks, check for sediment accumulation, and assess the overall condition of the tank. It’s also important to keep an eye on components like UV lights or pumps to confirm they’re working correctly. Don’t forget to clean the tank’s inlet and outlet screens to keep everything running smoothly.
Regular maintenance not only helps your system collect water more efficiently but also prolongs its lifespan, ensuring it continues to perform well for years to come.
Is it safe to use filtered rainwater on edible plants, and how can I check its quality?
Filtered rainwater can be a safe option for watering edible plants, but it’s important to be aware of potential health risks. Rainwater can sometimes pick up contaminants such as heavy metals, bacteria, or chemicals from roof surfaces or collection systems. Without proper filtration and maintenance, these pollutants could affect both the plants and the people who consume them.
To keep your rainwater safe, make it a habit to test it regularly with a water testing kit. Check for bacteria like E. coli, pH levels, and heavy metals. Additionally, routine maintenance - like cleaning filters and gutters - can significantly reduce contamination risks and ensure your rainwater remains suitable for irrigation.
Related posts
Related Articles

How AI Maps Pest Trends for Better Control
Explore how AI is revolutionizing pest control with accurate predictions, eco-friendly practices, and smarter pest management strategies.

What Is Green-on-Green Spray Technology?
Explore how green-on-green spray technology revolutionizes weed control by using AI for precise herbicide application, reducing chemical use significantly.

AI Models for Compost Decomposition Rates
Explore how AI models are revolutionizing composting by enhancing efficiency, reducing costs, and improving compost quality through real-time monitoring and predictions.

Unlock Your Green Thumb with Home Depot Garden Club: Benefits, Tips, and Community
Discover the exclusive benefits of joining the Home Depot Garden Club, including expert gardening tips, discounts, and a thriving online community. Explore the latest gardening trends and statistics to elevate your gardening experience.

AI Watering Schedules for Drought Conditions
AI-driven irrigation systems optimize water use during droughts, improving plant health and conserving resources through real-time data and machine learning.

How Calibration Impacts Monitoring Accuracy
Effective calibration of monitoring tools is essential for accurate data, reducing pesticide use, and ensuring healthy crop management.