Low Voltage Lighting vs. Solar Lighting

When deciding between low voltage and solar lighting for your garden, the right choice depends on your needs for brightness, reliability, and cost. Here’s a quick summary:
- Low Voltage Lighting: Offers consistent, bright illumination regardless of weather. It’s ideal for large spaces, security, and long-term use. However, it requires wiring, professional installation, and higher upfront costs ($100–$300 per fixture). Monthly operating costs are minimal (~$1.82 for 20 lights running 6 hours nightly).
- Solar Lighting: Powered by sunlight, it’s affordable ($10–$50 per light), easy to install, and eliminates electricity costs. Best for decorative purposes and small areas. Performance depends on sunlight, with reduced brightness on cloudy days. Batteries may need replacement every 1–3 years.
Quick Comparison:
| Feature | Low Voltage Lighting | Solar Lighting |
|---|---|---|
| Brightness | 100–1,200 lumens | 50–300 lumens |
| Reliability | Works year-round | Weather-dependent |
| Upfront Cost | $100–$300 per light | $10–$50 per light |
| Operating Cost | ~$1.82/month (20 lights) | $0 |
| Lifespan | 10–15 years (LED bulbs) | 1–3 years (batteries) |
| Installation | Requires wiring/trenching | Simple DIY setup |
Key Takeaway: Choose low voltage for reliable, long-term lighting and security. Opt for solar if you want a budget-friendly, flexible solution for ambient lighting in areas with plenty of sunlight.
Low Voltage Lighting: How It Works and What to Expect
How Low Voltage Lighting Works
Low voltage lighting operates on just 12 volts, a safer level achieved by using a transformer to step down the standard 120V household current. This makes it ideal for outdoor applications like garden lighting [5].
Here’s a quick breakdown of the system’s main components:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Transformer | Converts household voltage (120V) to 12V. |
| Wiring | Links the transformer to the light fixtures. |
| Light Fixtures | Includes options like path lights, spotlights, and underwater lights. |
| Bulbs | Often LED for better energy savings and durability. |
LED bulbs are a popular choice for these systems since they’re energy-efficient and long-lasting [3]. Plus, you can add photocells and timers to automate when your lights turn on and off, such as from dusk to dawn [5]. When setting up your system, make sure the transformer can handle the wattage of all connected fixtures and use the right wire gauge to ensure uniform brightness [5].
Now, let’s look at why this lighting system is a great addition to your outdoor space.
Benefits of Low Voltage Lighting
Low voltage lighting comes with a host of advantages. For starters, LED bulbs used in these systems can cut energy costs by up to 85% compared to traditional lighting [3]. On average, households using low-voltage LED lights could save about $100 annually on electricity [8].
Durability is another major plus. LED lights in low voltage setups can last up to 40,000 hours, far outlasting halogen bulbs, which typically need replacing after about two years [4].
These systems also offer incredible design flexibility. You can experiment with different lighting techniques like uplighting, downlighting, or path lighting to create stunning effects. As Mark Piantedosi, owner of Commonwealth Landscape Lighting, puts it:
"You want pools of light to guide your eye from one plant to the next, not continuous illumination." [4]
Safety is another big benefit. With only 12 volts of power, the risk of electrical shock is significantly reduced [6]. Plus, the compact bulbs and wiring can fit into tight spots where traditional fixtures might not work [7]. And let’s not forget security - well-lit outdoor areas can deter burglars. In fact, studies show that over 30% of home burglaries are linked to poor outdoor lighting [8].
With all these benefits, it’s worth considering what’s involved in the installation process and the potential costs.
Installation Requirements and Costs
Setting up a low voltage lighting system often requires a notable upfront investment, and many homeowners opt for professional installation. On average, professional installation costs range from $100 to $150 per fixture [10][11][13]. For a complete project, expenses typically fall between $800 and $6,000, depending on the size of your yard and the number of fixtures [13].
Here’s a closer look at the costs:
- Lighting fixtures: $42–$100 per fixture
- Basic labor: $108–$168 per fixture
- Job supplies: $4–$5 per fixture
This brings the total cost to about $229–$389 per installed fixture [9].
Additional costs include transformers ($200–$500) and wiring, which runs around $3–$5 per foot [11][13]. If trenching is needed for underground wiring, expect to pay between $5 and $13 per linear foot [11].
While simpler systems might be manageable as a DIY project, more complex or hardwired setups should be handled by a licensed electrician. This ensures safety and compliance with electrical codes. For example, low-voltage cables need to be buried at least six inches deep to maintain consistent brightness and reduce hazards [4][5].
Specialty contractors typically charge $3,000–$3,500 for a ten-light system, while non-specialty contractors might complete similar work for around $2,670 [12]. Though the initial costs may seem steep, the energy efficiency and long-term savings make it a worthwhile investment.
Solar Lighting: How It Works and What to Expect
How Solar Lighting Works
Solar lighting stands apart from low-voltage systems by eliminating the need for wiring and transformers. Instead, it uses sunlight to power LED lights through a photovoltaic cell. During the day, this cell captures solar energy and charges a battery, which then powers the lights at night. A built-in light sensor ensures the lights automatically turn on at dusk and off at dawn.
Here’s a closer look at how the components work together:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Solar Panel | Converts sunlight into electrical energy using photovoltaic cells. |
| Rechargeable Battery | Stores the energy collected during the day for use at night. |
| LED Light Source | Provides illumination using the stored energy. |
| Control Circuit | Oversees charging, light activation, and power distribution. |
| Light Sensor | Detects ambient light levels and controls when the lights turn on/off. |
A few key details: Monocrystalline panels are particularly effective in low-light conditions [21]. Rechargeable batteries, such as NiMH, are known for their reliability, while lithium-ion batteries offer higher storage capacity but may be less effective in extreme temperatures [14]. For best results, solar lights require 6 to 8 hours of direct sunlight to fully charge [14], making proper placement critical.
Benefits of Solar Lighting
Solar lighting offers several perks, especially for gardens. First, it’s cost-effective. Solar lights are generally less expensive upfront than low-voltage lighting and add nothing to your electricity bill [15]. They’re also easy to install - no wiring or professional help required - and can be rearranged as your garden layout evolves [15]. Additionally, solar lights use renewable energy and operate at low voltage, making them both environmentally friendly and safe [15].
Drawbacks and Performance Issues
While solar lighting has its advantages, it’s not without its challenges. One common issue is brightness. Solar garden lights typically produce less light than plug-in options, making them better suited for creating ambiance rather than strong illumination [14]. Weather is another factor. Shorter days and less sunlight in winter can reduce their effectiveness [17], and overcast skies may limit energy capture, sometimes reducing output to as low as 10% to 60% [18][19].
If solar lights don’t receive enough sunlight, they may dim or switch to a power-saving mode to conserve battery life [19]. Shading from trees or buildings can decrease energy output by up to 25% [19][21]. Other factors, like dirt or debris on the panels and battery wear, can also impact performance [16].
Sandeep Yadav, Planning Engineer at the Gas Authority of India Limited, highlights the importance of sunlight for optimal performance:
"Solar lights require sunlight to charge their batteries throughout the day, so they can function optimally at night." [20]
These limitations and performance variances set the stage for a detailed comparison in the next section.
Side-by-Side Comparison: Energy Use, Costs, and Performance
Feature Comparison Chart
Here's a breakdown of how low voltage and solar lighting stack up in terms of energy use, costs, and performance:
| Feature | Low Voltage Lighting | Solar Lighting |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Consumption | Uses LED bulbs with minimal energy use [1] | Powered by sunlight; performance depends on weather [1] |
| Monthly Operating Cost | Around $1.82/month for 20 LED lights (6 hours nightly) [23] | $0 – no electricity costs [2] |
| Upfront Cost | $100–$150 per light with installation [24] | $50–$200 per light [24] |
| Brightness Output | 100–1,200 lumens per fixture [27] | 50–300 lumens per fixture [27] |
| Lifespan | 10–15 years (LED bulbs) [1] | 1–3 years (batteries degrade over time) [28] |
| Weather Dependence | Reliable performance year-round [25] | Reduced output on cloudy or overcast days [26] |
| Installation Complexity | Requires trenching and wiring [2] | Simple DIY setup [15] |
This comparison highlights key differences. For instance, low voltage systems use up to 75% less energy and cost about $1.82 per month to run 20 lights for 6 hours nightly [1][23]. On the other hand, solar lights eliminate electricity costs entirely but deliver less brightness and depend heavily on sunlight, with cloudy days significantly affecting performance [26].
Durability is another key factor. Low voltage lights often feature robust materials like brass or aluminum, offering decades of use with proper care. They also typically achieve an IP65 or higher weather resistance rating, ensuring reliable outdoor performance [28]. Solar lights, however, often rely on plastic components and may need replacement after just a few seasons [28]. Additionally, the batteries in solar systems generally require replacement every 5–7 years, adding approximately $1,000 per cycle [2][12].
Best Uses for Each Lighting Type
Low voltage lighting is the go-to choice for areas requiring consistent, high-intensity lighting. It’s perfect for security lighting around entryways, pathways for safe navigation, and accent lighting to showcase garden features. Thanks to its reliable power source, it performs well in larger outdoor spaces where steady, dependable light is a must [27]. Plus, these systems integrate seamlessly with timers, motion sensors, and smart home controls, offering added convenience and energy efficiency [25].
Solar lighting, by contrast, shines in more ambient settings. Its softer illumination works well for highlighting small garden accents, outlining flower beds, or providing temporary lighting that can be moved as needed. It’s particularly useful in remote areas of your yard where wiring isn’t practical, making it a popular choice for seasonal decorations or rental properties [15]. However, solar lights perform best in areas with abundant sunlight. Heavy tree cover or frequent cloud cover can limit their effectiveness [26].
Ultimately, the choice between these lighting options depends on your priorities. Low voltage systems deliver long-term reliability and advanced control, making them ideal for functional and security-focused lighting. Solar lights, on the other hand, offer a flexible, cost-effective solution for creating a warm, inviting atmosphere in your garden. Whether you need dependable brightness or adaptable ambiance, both options have their place in outdoor lighting design.
sbb-itb-4d6a8dd
🚀 Ready to Reinvent Your Garden?
Join thousands of homeowners who have transformed their gardens using our AI design tool. Upload one photo to explore endless possibilities.
Get your AI garden designs →Solar VS Low Voltage LED Lights - Garden LED WATT BRIGHTNESS COMPARISON and Buying Tips

How to Choose the Right Lighting for Your Garden
Selecting the perfect lighting for your garden comes down to understanding your specific needs and priorities. Whether you opt for low voltage or solar lighting depends on factors like garden size, brightness requirements, budget, and even environmental considerations. Here's a breakdown to help you decide what works best for your outdoor space.
Garden Size:
For smaller gardens, solar lights are a great choice. They provide a soft, ambient glow that works well for accenting pathways or highlighting specific features. On the other hand, if you’re dealing with a larger yard or need widespread illumination, low voltage systems are more reliable. They deliver consistent brightness, making them ideal for expansive areas [29].
Brightness Requirements:
If security is a priority, low voltage lighting is the way to go. These systems excel in providing bright, dependable light for entryways, pathways, and even architectural highlights [29]. For a more decorative touch, solar lights are perfect - they create a gentle ambiance, ideal for smaller spaces or garden accents [29].
Budget and Installation:
Solar lights are more affordable upfront, typically costing $10 to $50 per unit, while low voltage fixtures range from $100 to $300 each. However, durability and long-term costs differ. Solar lights usually last 1–3 years due to battery wear, whereas low voltage LED bulbs are rated for 20,000–50,000 hours [31]. Solar lights are also easy to install, making them a favorite for renters or quick DIY projects. In contrast, low voltage systems require more planning and often professional installation, but they integrate seamlessly with timers, motion sensors, and smart home systems once set up [31].
Environmental Goals:
For those prioritizing renewable energy, solar lights are an obvious choice since they don’t add to your electricity bill [29]. That said, low voltage LED systems are impressively energy-efficient, producing 65 to 90 lumens per watt - about five times more efficient than traditional bulbs [30].
Weather Dependence:
Solar lights rely heavily on sunny days to perform well, while low voltage systems deliver consistent results regardless of weather conditions [29].
Ultimately, if you’re looking for dependable security lighting, low voltage systems are a solid option. For decorative accents or seasonal touches, solar lights provide flexibility and affordability. Many homeowners find a combination of both works best - for example, using low voltage lights for main pathways and solar lights for garden beds or festive decorations.
Planning Your Lighting Design with AIGardenPlanner
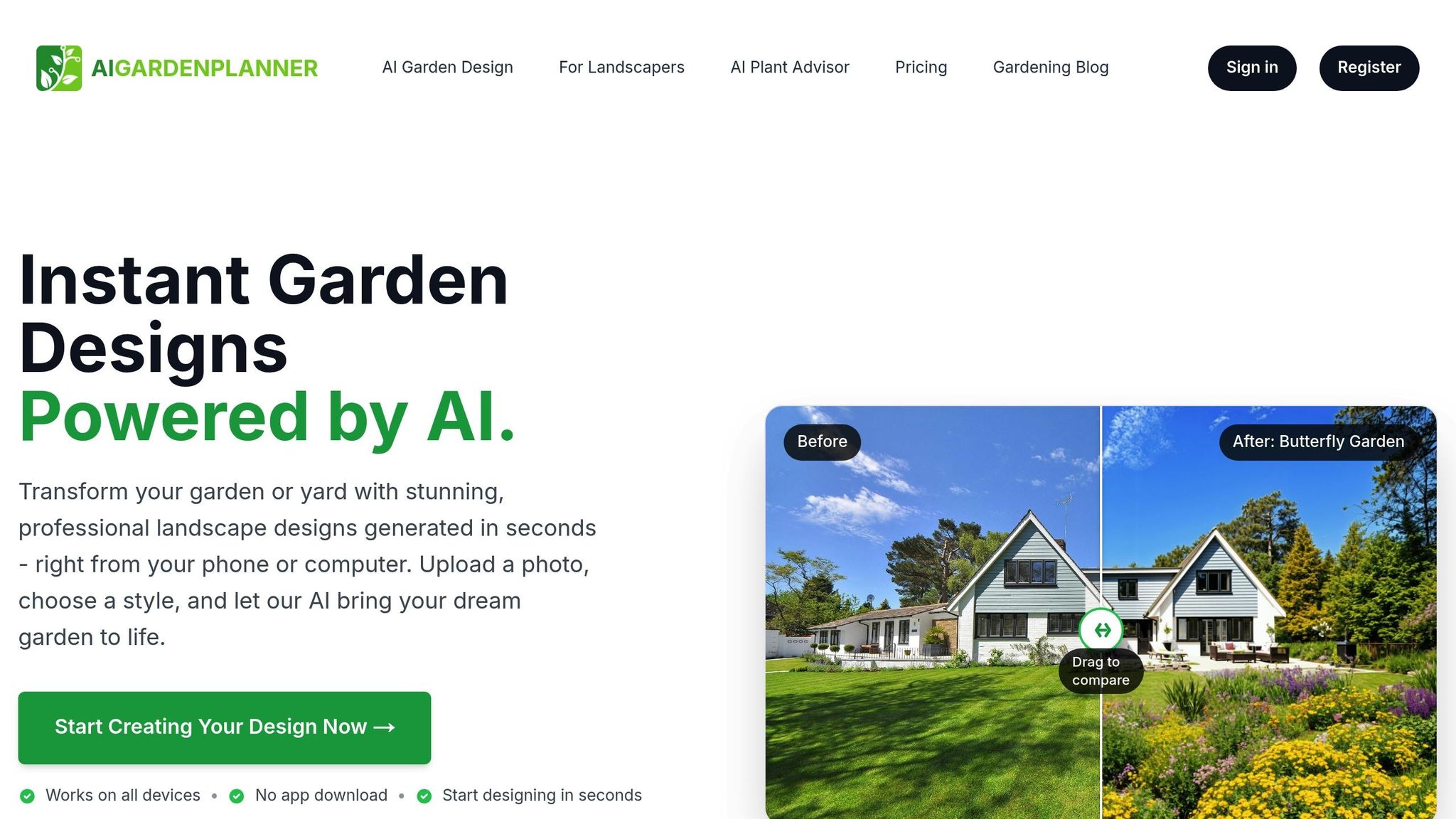
Once you’ve narrowed down your lighting options, tools like AIGardenPlanner can help you bring your vision to life. This AI-powered platform allows you to upload photos of your garden and experiment with different lighting placements. You can see how low voltage and solar lighting options enhance your space, making it easier to finalize your design.
The platform’s AI Plant Advisor even factors in your location and climate when suggesting lighting solutions. This is especially helpful for solar lighting, as sunlight exposure and weather conditions can significantly impact its performance. Whether you’re in a sunny region or an area prone to overcast skies, the tool ensures your lighting choices align with local conditions.
With over 50 garden styles to explore, AIGardenPlanner helps you visualize how lighting complements different themes. For instance, low voltage lighting might suit a sleek, modern design, while solar lights can add charm to a cottage-style garden. Once your design is ready, you can download high-resolution plans to share with electricians or landscapers, ensuring professional installations match your exact vision.
Additionally, AIGardenPlanner offers detailed growing guides that include seasonal lighting tips. This ensures your lighting system not only enhances your garden’s aesthetics but also supports the health and growth of your plants throughout the year. By integrating lighting design with plant care, you can create a garden that thrives both visually and functionally as it matures.
Final Thoughts: Making the Right Choice
When deciding on the best lighting for your garden, weigh energy efficiency, cost, and performance. Each option has its strengths, and understanding their trade-offs will help you make the most informed decision.
Low voltage LED systems are incredibly energy-efficient, using up to 75% less energy, while solar lights rely on renewable energy, eliminating ongoing electricity costs entirely [1][22]. That said, solar lighting can be unpredictable, as its performance depends on weather conditions. In contrast, low voltage systems provide consistent brightness no matter the weather [32].
Cost is another key factor. Solar lights are more affordable upfront, ranging from $10 to $50 each, but their lifespan is limited to about 1–3 years due to battery wear [31]. On the other hand, low voltage systems are more expensive, costing $100 to $300 per light [31], but they offer long-term value. LED bulbs in these systems can last between 20,000 and 50,000 hours - up to 17 years if used for 8 hours a night [33]. As for operating costs, a 20-light low voltage LED system costs roughly $1.82 per month, or $21.84 annually [23].
When it comes to performance, the difference is clear. According to an electrician:
"With wired, the lumen output stays fairly strong and doesn't deteriorate below 70% until some time after 50,000 burn hours. That's 8 hours a night for 17 years." – jtraf, Electrician [33]
By contrast, many users report a noticeable decline in solar lights' performance over time. This is why professionals often recommend wired low voltage systems for their reliability and consistent output [33].
Maintenance requirements also vary. Solar lights need regular cleaning of their panels and periodic battery replacements, while low voltage systems are largely maintenance-free after installation [1]. Additionally, low voltage lighting provides the brightness needed for security purposes, helping to deter intruders. Meanwhile, solar lights are better suited for decorative accents and creating a soft, ambient glow [32].
When planning your garden lighting, consider how these insights fit into your overall design. Tools like AIGardenPlanner can help you visualize the impact of different lighting options. The platform's AI Plant Advisor takes your location and climate into account, which is particularly helpful for solar lighting where sunlight exposure is a factor. With over 50 garden styles to explore, you can see how lighting enhances your space and even download high-resolution plans to share with your installers.
FAQs
What’s the best choice for garden lighting: low voltage or solar, especially for a mix of large and small spaces?
When deciding between low voltage lighting and solar lighting, it all comes down to the size and purpose of your garden. If you’re working with a larger space, low voltage lighting is your best bet. It offers brighter, more dependable light, making it perfect for pathways, expansive lawns, or showcasing standout features. While the initial cost might be higher, it’s energy-efficient and built to last.
For smaller or decorative areas, solar lighting is a solid choice. It’s budget-friendly, simple to set up, and doesn’t require wiring, which makes it ideal for accent lighting or temporary arrangements. Keep in mind, though, that solar lights tend to be less bright and may not hold up as well in shaded or cloudy conditions.
If your garden has a mix of large and small spaces, why not combine the two? Use low voltage lighting for the bigger areas and solar lights for decorative touches. This way, you’ll strike a balance between cost, functionality, and ease of use.
What kind of maintenance is required for solar lights compared to low voltage lights?
When it comes to upkeep, solar lights are relatively easy to manage. You'll need to replace their batteries every 1–2 years and keep the solar panels clean to prevent dirt and debris from affecting their performance. However, it's worth noting that the batteries may wear out faster than other parts of the system over time.
In contrast, low-voltage lighting systems require a bit more attention. Maintenance tasks include cleaning the fixtures, replacing bulbs, inspecting the wiring, and occasionally checking or repairing the transformer. With regular care, these systems can last anywhere from 5–10 years or more, making them a durable option, albeit one that comes with slightly higher maintenance needs compared to solar lights.
Can I connect low voltage lighting to smart home devices for automated control?
Yes, you can often connect low voltage lighting systems to smart home devices for automated control. Many of today’s systems are built with smart automation in mind, making it possible to manage your lights through apps, voice assistants, or smart home platforms. This means you can easily set schedules, tweak brightness levels, and create the ideal atmosphere for your garden - all with a few taps or simple voice commands.
When choosing a system, check for compatibility with well-known smart controllers to ensure it works smoothly with your current smart home setup.
🎨 Visualize Your Dream Garden Today!
Transform any outdoor space into a professional landscape design in minutes. Just upload a photo, choose your style, and let our AI do the rest.
Start your garden transformation now →Related posts
Related Articles

A Complete Guide to Building a Stunning Rock Garden Border
Enhance your outdoor space with a beautiful rock garden border. Learn how to choose materials, design, and maintain your rock garden border effectively.

AI Research on Frost-Resistant Crops
Explore how AI is revolutionizing the development of frost-resistant crops, benefiting both farmers and home gardeners with tailored solutions.

How AI Analyzes Irrigation System Compatibility
Explore how AI optimizes irrigation systems by analyzing soil, weather, and plant data, leading to efficient water use and healthier gardens.

AI Data Analytics for Climate-Resilient Gardens
Explore how AI data analytics can enhance gardening practices, from pest management to resource optimization, for climate-resilient gardens.

Ultimate Guide to Zen Garden Water Feature Care
Maintain the serenity of your Zen garden water feature with essential cleaning, seasonal care, and troubleshooting tips for lasting beauty.

AI Climate Data for Garden Planning
Explore how AI tools transform garden planning with tailored plant recommendations, weather insights, and sustainable designs for thriving ecosystems.